In 1986, the Federal government started a program to encourage private investors to develop and manage affordable housing under the Tax Reform Act of 1986. The incentive created under this program is a tax credit that investors can use to offset their income tax liability dollar for dollar to increase the investors’ internal rate of return on their investment.
This credit is called the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit and is governed under Section 42 of the Internal Revenue Code. Congress has delegated the administration of low-income housing tax credits to the states.
Why would the government need to give an incentive to encourage investment in affordable housing? Due to the restrictions on the amount of rent allowed to be charged, manyaffordable housingprojects will not produce a positive cash flow until the project is in maturity. The purpose of affordable housing is to provide safe, decent, stable and affordable housing for vulnerable families and individuals. These include, but are not limited to, families and individuals who earn below the poverty guideline, disabled individuals and elderly citizens.
There is a high demand for affordable housing, and the cost of living in many major cities continues to rise. According to the National Low-Income Housing Coalition, there is a shortage of affordable housing available for extremely low-income renters. See below for a summary of the shortage for several key states:
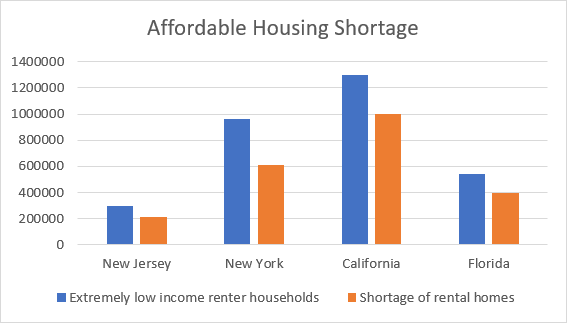
The chart above shows the level of demand by comparing the number of extremely low-income renters (in blue) and the lack of rental homes (orange). California alone has a shortage of almost a million rental homes.
But why invest ifthere issuch a delayinpositive cash flow fordevelopers and investors? Although this delay is not very attractive, many capital investors rely on the low-income housing tax credits as a way to increase their rate of return on the projects and help to overcome the perceived risk of investing in affordable housing. There are many other benefits to affordable housing besides the low-income housing tax credits. Some of these benefits include:
- Social impact: Helping those in need by providing housing and reducing the level of homelessness.
- Financing benefits: There are federal, state and local financing options with favorable rates and payment terms, as well as state and local grants offered specifically to affordable housing projects. There is usually a restriction on the use for a period of time as stipulated by the states.
- Tax benefits: Many capital investors receive additional tax savings due to the depreciation deduction from the projects.
- Other benefits: Many counties and cities offer real estate tax exemptions or abatements to help reduce project costs.
- Guaranteed collectability of rents: Most low-income housing projects also receive rental subsidies from federal and state governments. These payments are pretty much guaranteed each month as long as the subsidy requirements are met.
- Development benefits: Project developers are allowed fees for services to develop the project, which provides another income stream.
Effective planning is not only the first step, but it is critical to maximizing the credits and benefits available for low-income housing credit projects. Understanding the state program requirements, available financing and other benefits can help maximize profits on projects as a whole.
Author: Samantha Hoyte, CPA, CFE, [email protected]
contact a member of the Real Estate Services Group.
Real Estate Services


