How does one speak Microsoft Power BI? What do I even mean? In the world of data visualization and business intelligence software, much of the same words are used
but have different meanings based on the platform you are referring to. When working with clients used to other software platforms, I keep finding confusion on both sides that can prohibit the smooth progress of a Power BI project because we are not speaking the same language. If you are fully new to the world of data visualization and analytics, then this will help you understand what others are talking about.
If you are experienced with other data visualization software, the following will help you feel more comfortable discussing and understanding Power BI’s language. No matter your level of knowledge within the world of data, I hope that I can make it easier for you to navigate the Power BI universe.
The Three Ps – Power BI Desktop, Power BI Service, Power BI Mobile
Microsoft Power BIis the catch-all phrase used to describe Microsoft’s data visualization and business intelligence platform. It consists of Power BI Desktop, Power BI service, and Power BI Mobile. You, as the user, could use all three elements down to only one based on what you are trying to accomplish and how you are consuming your data. For most, your first exposure to Microsoft Power BI will be with the use ofPower BI Service. This is an online SaaS (Software as a Service) that contains many of the same capabilities as Power BI Desktop but is hosted in the cloud, supports sharing with colleagues, and automatically keeps your reports and dashboards up to date. You will often find Power BI Service also referred to as Power BI online.Power BI Mobileties into the service in that it is an app available on iOS, Android, and Windows mobile devices. Power BI reports can be designed for optimal use on a computer and/or for a mobile device screen. For an organization implementing Power BI, the least likely element used will bePower BI Desktop. Desktop is most often used by those individuals designing the Power BI reports that will be used for your organization. Power BI Desktop has the most capabilities and flexibility when pulling in data from many sources, analyzing it, and then building reports to consume the data.
If you are a bit confused, just stick with me! Simplified, your Power BI experts will use Power BI Desktop to build a report from your data. That report will then be published to the Power BI Service, a dashboard might be created too, and shared with your team members. Lastly, if you want your users to be able to easily use the report on the Power BI Mobile app, you would have the report creator make sure the initial report is designed for both desktop and mobile viewing. If you receive a request for major changes to the report, either you or the report designer will mostly likely make those changes in Power BI Desktop and push it to replace the previous report on the service (if named the same and using the same data sources, your settings in Power BI service will stay in place for the replaced report).
Building Blocks of Power BI
Now I’ll get to quite a few words and phrases that are the “building blocks” of Power BI and what they mean for you:
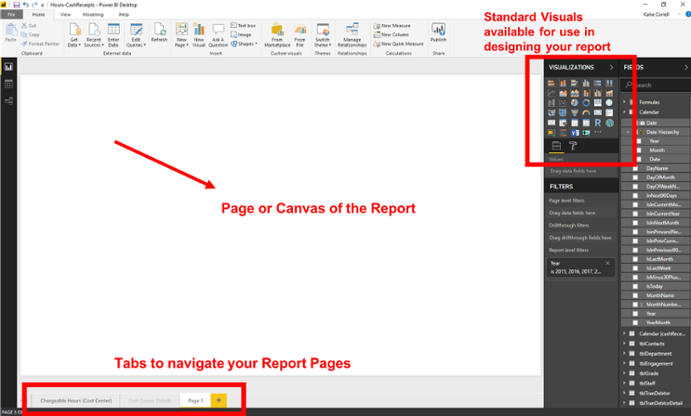
Visuals(or visualizations) – these are the bar graphs, scatterplots, tables, pie charts, maps, and more that visually represent the data that you’ve pulled into Power BI. Visuals are the elements that provide the means for you to tell a story with your data and the pages of your Power BI report.
- You’ll find that each visual is contained within a rectangular box, and this might be a little confusing, but each visualization can also be referred to as aTile. More often than not, you’ll only really find a visual referred to as a tile when talking about dashboards.
Dataset– this is the collection of data that you’ll use in visuals to tell a story with your data. Datasets can be as simple as an Excel spreadsheet or as complicated as a combination of SQL server tables, a Google sheet used to capture Twitter mentions, that Excel doc, Google Analytics data, and the online results of a marketing campaign. From simple to complex, your dataset will be the basis of your report and subsequent dashboard.
Report– This is the backbone of Power BI. The vast majority will pull in their data and create a report with multiple pages featuring lots of visuals in both Power BI Desktop and Power BI Service. The file type is.PBIX, and this is what you publish to the Power BI Service. One way to visualize a Power BI report is to think of it as a PowerPoint presentation with however many slides you need BUT that presentation is a Power BI report, and those slides arePageswith navigation tabs on the bottom for you to move between your report pages. If you are familiar with other data visualization software, you may find yourself calling this a dashboard but that is confusing for anyone in the Power BI universe.
- A single blank page can also be referred to as acanvasor the blank backdrop where you place visualizations.
Dashboard– this can only be created in the Power BI Service from reports. Consider a dashboard as a high-level summary of your dataset(s). This dashboard is a single “page” with visuals from a single report OR multiple reports. Dashboards are meant to provide quick insights in the data you have presented in your report(s). The visuals of the dashboard can also be referred to as tiles so hopefully this isn’t adding to any confusion you might be experiencing at this point!
There are still so many words and phrases that need to be defined so that you can become fluent in Power BI, but I’ll leave those for a second and third post. I hope that just having an easy-to-understand explanation on the building blocks of Power BI, you’ll feel more confident and secure in discussing and understanding Microsoft’s data visualization and business intelligence software platform.
Keep an eye out for the next post onHow to Speak Power BI: Intermediate Vocabulary.
Ready to speak to a Power BI expert about your project?Contact us onlineor give us a call at240-406-9960.



