Distinguishing a Contribution Versus an Exchange Transaction
Distinguishing a contribution versus an exchange transaction can be difficult and even overlooked. Grants, membership dues and sponsorships are terms that are broadly used to refer not only to contributions but also to assets transferred in exchange transactions. The underlying substance of the transaction will be the indicator that drives proper accounting and reporting.
FASB Accounting Standard Codification (“FASB ASC”) 958-605-20 Glossary defines contributions, inherent contributions, and exchange transactions as follows:
- Contribution – An unconditional transfer of cash or other assets to an entity or a settlement or cancellation of its liabilities in a voluntary nonreciprocal transfer by another entity acting other than as an owner. In a contribution transaction, the value, if any, returned to the resource provider is incidental to potential public benefits.
- Exchange Transactions – Reciprocal transfers in which each party receives and sacrifices approximately equal value. In an exchange transaction, the potential public benefits are secondary to the potential proprietary benefits to the resource provider.
- Inherent Contribution – A contribution that results if an entity voluntarily transfers assets (or net assets) or performs services for another entity in exchange for either no assets or for assets of substantially lower value and unstated rights or privileges of a commensurate value are not involved.
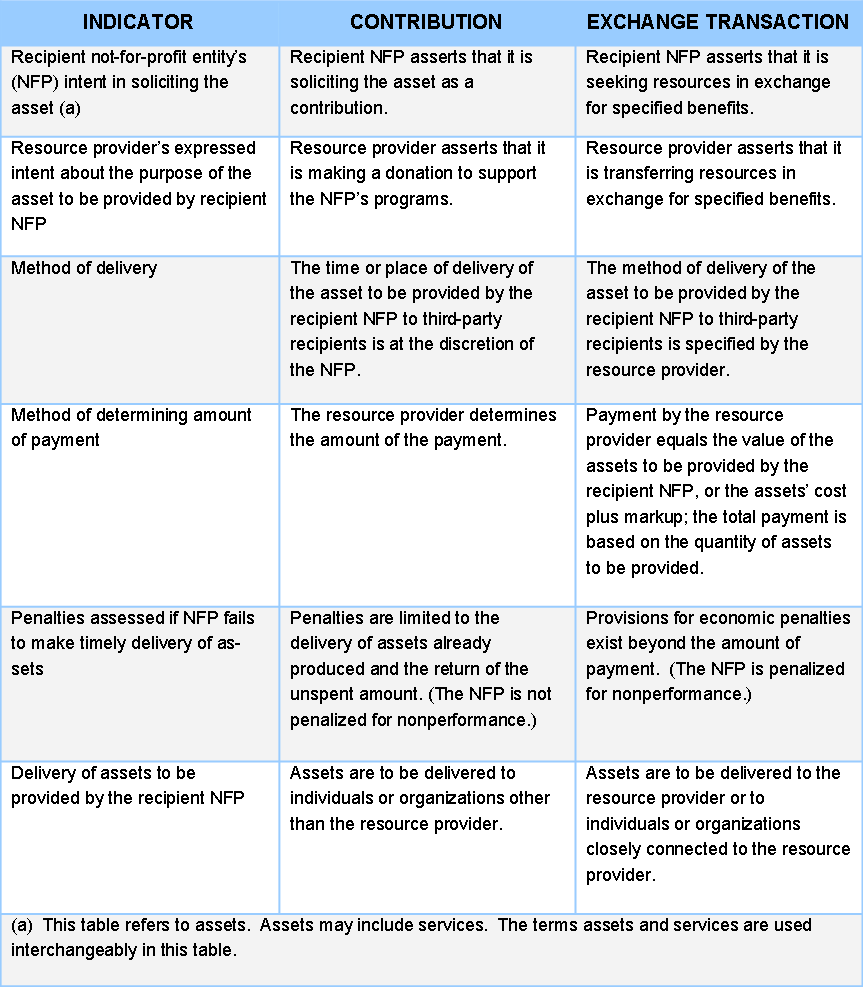
A careful assessment of the characteristics of the transaction, from the perspectives of both the resource provider and the recipient, is necessary to determine whether a contribution has occurred. FASB ASC 958-605-55 includes the table on the following page as a resource with indicators that may be helpful in determining whether individual asset transfers are contributions, exchange transactions, or a combination of both.
No single indicator in the table above is determinative for classification as a contribution or exchange transaction and some indicators may be more significant than others.
REVENUE RECOGNITION
Revenue from exchange transactions follows generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). For example, revenue derived from membership dues in exchange transactions shall be recognized over the period to which the dues relate.
With certain exceptions and subject to guidance regarding promises to give being unconditional or conditional, contributions shall be recognized as revenues in the period received and as assets, decreases of liabilities, or expenses depending on the form of the benefits received.